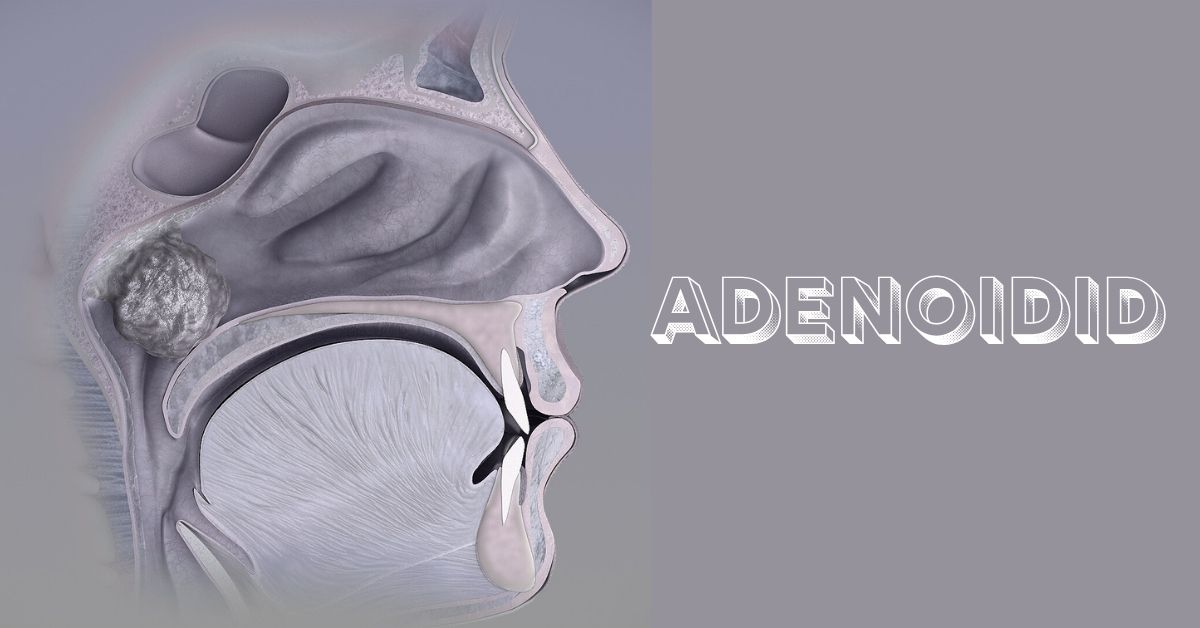
Adenoidid, commonly known as adenoid inflammation or adenoiditis, is a condition that often affects children but can also occur in adults. It involves the swelling and infection of the adenoids—small glands located at the back of the nasal passage that play a crucial role in the immune system. Although these glands are part of the body’s defense mechanism, they can become problematic when inflamed, leading to discomfort, difficulty in breathing, and even recurrent infections. Understanding adenoidid is essential for timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and overall respiratory health.
What Are Adenoids
Adenoids are lymphatic tissues that are part of the body’s immune system. Situated high in the throat behind the nose and the roof of the mouth, adenoids help trap germs entering through the nose and mouth. In young children, they play a vital role in building immunity by fighting off infections. However, as people age, the adenoids naturally shrink and become less important since the body develops other defense mechanisms. When adenoids become inflamed or infected, the condition is referred to as adenoidid or adenoiditis, which can cause significant breathing and sleeping issues.
How Adenoidid Develops
Adenoidid develops when bacteria, viruses, or allergens irritate the adenoid tissue, leading to inflammation. It commonly occurs after upper respiratory infections or chronic sinus issues. The infection causes the adenoids to swell, which can block the nasal airways, leading to mouth breathing and snoring. In some cases, recurrent infections can cause the adenoids to remain enlarged even after recovery, resulting in chronic adenoiditis. If left untreated, this can affect a child’s speech development, hearing, and facial growth due to prolonged breathing difficulties.
Common Causes of Adenoidid
Adenoidid can be triggered by several factors, including bacterial infections such as Streptococcus or viral infections like influenza, rhinovirus, or adenovirus. Allergies are another significant contributor, as constant exposure to allergens can cause persistent irritation and swelling. Environmental factors like pollution, smoke, and dry air also play a role in worsening the condition. In children with weakened immune systems, adenoidid may become a recurring issue, necessitating medical evaluation and sometimes surgical intervention.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Adenoidid
The symptoms of adenoidid can vary depending on the severity and duration of inflammation. Common signs include nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, and a nasal-sounding voice. Many children with adenoidid prefer to breathe through their mouths, leading to dry mouth and bad breath. Chronic ear infections, hearing problems, and frequent sore throats can also be indicators of swollen adenoids. In severe cases, children may experience sleep disturbances such as sleep apnea, which can impact overall health and development.
Adenoidid in Children
Children are more prone to adenoidid due to their developing immune systems and larger relative adenoid size. In early childhood, the adenoids are active in protecting the body from pathogens, but they can also become easily infected. Recurrent adenoidid can lead to constant nasal blockage, middle ear infections, and even changes in facial structure—sometimes known as “adenoid face,” characterized by an open mouth, long face, and dull expression. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent such complications and ensure healthy growth.
Adenoidid in Adults
Although rare, adults can also suffer from adenoidid. In most cases, it occurs due to chronic sinus infections, allergies, or immune deficiencies. Persistent nasal obstruction, postnasal drip, and snoring are typical symptoms in adults. Sometimes, an enlarged adenoid in adults may indicate more serious conditions such as chronic infection or, in rare cases, malignancy. Therefore, it’s crucial for adults experiencing persistent nasal blockage to seek medical attention for a thorough examination.
How Adenoidid Affects Breathing and Sleep
One of the most noticeable effects of adenoidid is on breathing and sleep quality. Swollen adenoids obstruct airflow through the nasal passages, forcing individuals to breathe through their mouths. This not only leads to dry throat and bad breath but also disrupts normal sleep patterns. Mouth breathing can cause snoring and, in severe cases, sleep apnea—a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. Over time, poor sleep can affect mood, concentration, and physical health, especially in children.
Diagnosing Adenoidid
Diagnosis of adenoidid usually begins with a physical examination by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. Doctors may use a small mirror or a flexible endoscope to inspect the adenoids. Imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans can provide additional insights into the size and condition of the adenoids. Sometimes, a sleep study may be recommended if sleep apnea is suspected. Accurate diagnosis is crucial because the symptoms of adenoidid can resemble other respiratory or sinus conditions.
Treatment Options for Adenoidid
Treatment for adenoidid depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, doctors often prescribe antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, along with nasal sprays to reduce swelling. Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can also provide relief. For chronic or recurrent adenoidid, surgical removal of the adenoids—known as adenoidectomy—may be recommended. This procedure is common and generally safe, helping to restore normal breathing and prevent further infections. Post-surgery, most children recover quickly and experience a significant improvement in sleep and breathing.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
While medical treatment is essential, home care can support recovery and prevent recurrences. Keeping the home air moist with a humidifier can ease nasal congestion. Encouraging children to stay hydrated helps thin mucus, making breathing easier. Avoiding allergens like dust, smoke, and pet dander can also prevent inflammation. Saline nasal rinses and steam inhalation are simple yet effective remedies for soothing the nasal passages. Maintaining good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, reduces the risk of infections that can cause adenoidid.
Preventing Adenoidid
Prevention focuses on minimizing exposure to infection and allergens. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals strengthens the immune system, making the body more resistant to infections. Regular physical activity and adequate sleep also promote immune health. Avoiding cigarette smoke and polluted environments significantly lowers the risk of nasal and throat infections. For children prone to recurrent adenoidid, regular ENT checkups can help catch early signs of inflammation before it becomes severe.
Complications Linked to Untreated Adenoidid
If left untreated, adenoidid can lead to several complications, including chronic ear infections, sinusitis, and sleep disorders. Persistent mouth breathing can cause dental problems and facial bone changes over time. In severe cases, it may affect speech development and concentration due to poor sleep quality. For these reasons, early medical attention and consistent monitoring are vital to avoid long-term issues and ensure a healthy respiratory system.
Post-Surgical Recovery and Care
After an adenoidectomy, patients typically experience mild throat soreness and nasal congestion, which subside within a few days. Doctors usually recommend a soft diet and plenty of fluids during recovery. Pain medication may be prescribed to ease discomfort, and rest is crucial to speed up healing. Parents should follow postoperative care instructions carefully, avoiding exposure to infections for at least a week. Most children resume normal activities within a short time, enjoying improved breathing and fewer infections afterward.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if you or your child experience persistent nasal blockage, loud snoring, frequent ear infections, or difficulty breathing during sleep. These could be signs of chronic adenoidid requiring medical attention. Early diagnosis not only prevents complications but also ensures more effective treatment. If symptoms persist despite medication, an ENT specialist can evaluate whether surgery is necessary for long-term relief.
Conclusion
Adenoidid is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact breathing, sleep, and overall well-being, especially in children. Recognizing its symptoms early and seeking medical help can prevent long-term complications and improve quality of life. Whether through medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery, effective management of adenoidid ensures a healthier respiratory system and better daily comfort. Being proactive about nasal and throat health is key to maintaining clear airways and a strong immune response.
FAQs
What is the main cause of adenoidid?
Adenoidid is mainly caused by bacterial or viral infections that lead to inflammation of the adenoid tissue.
Can adults suffer from adenoidid?
Yes, though rare, adults can develop adenoidid due to chronic infections, allergies, or immune issues.
How is adenoidid treated without surgery?
Mild cases can be treated with antibiotics, nasal sprays, and lifestyle adjustments to reduce inflammation.
Is adenoidectomy safe for children?
Yes, adenoidectomy is a common and safe procedure with a quick recovery time and lasting benefits.
How can adenoidid be prevented?
Good hygiene, a healthy diet, avoiding allergens, and regular medical checkups help prevent adenoidid.